The basis of a ketogenic diet is the elimination of carbohydrates from the daily menu and their replacement by fats. The ketogenic diet is used to treat epilepsy and is primarily recommended for patients who do not have the expected effects of pharmacology.
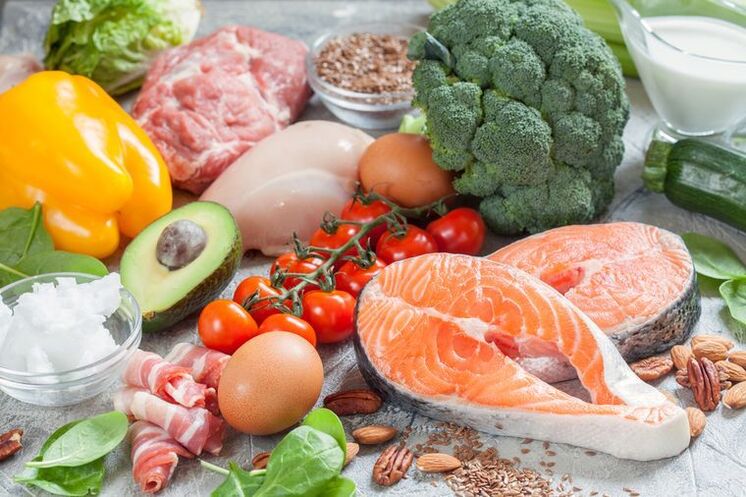

The main source of energy is carbohydrates, so we consume the most (about 50%). They contain 35% of fats and protein (about 15%) in the daily diet. When the body receives very little carbohydrate, it requires energy from the fats that form the basis of the ketogenic diet. Fat can be 80-90 percent.
Although the results are quick to use and people who use it after a few days notice the difference, this change does not last long. They are often malnourished and deprived of essential nutrients.
Contrary to appearances, the ketogenic diet is not the next "miracle" diet. This special menu is created for a specific purpose. Studies show that limiting carbohydrate intake to fat is ideal for people suffering from refractory epilepsy.
Diets for supportive therapy with oils, autism, Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, some types of epilepsy and encephalopathy are also considered.
Ketogenic diet - how does it work?
When fats are broken down into the body's main fuel, ketone bodies are formed: acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyric acid. They reach the nervous system, where they feed nerve cells instead of glucose.
Although metabolic changes in this diet are similar to those in hungry people, they have a beneficial effect on epilepsy. High concentrations of ketone bodies in the blood prevent the onset of seizures.